
Powering a Clean Energy Future with Uranium
Nuclear fission uranium gif free#
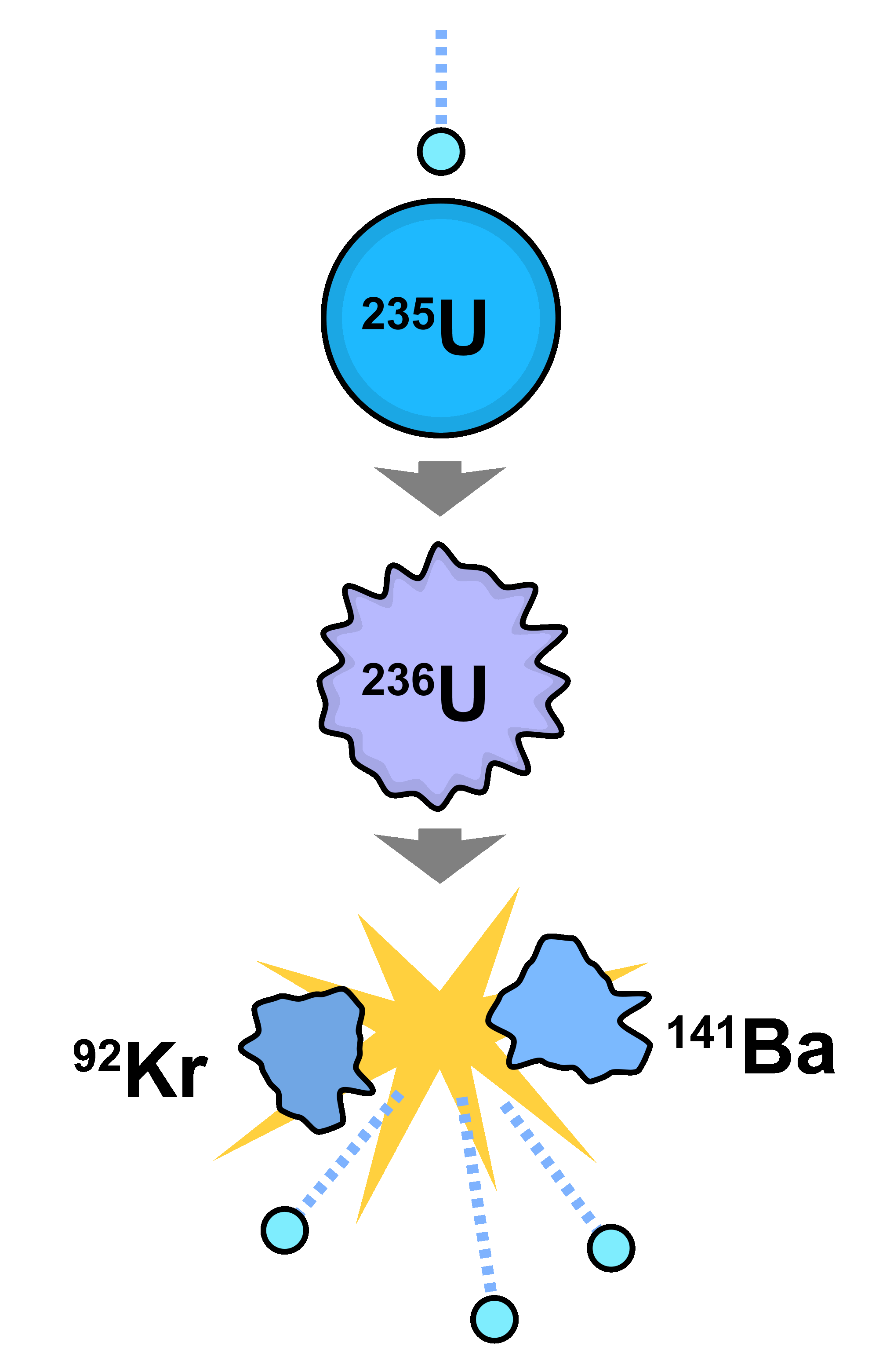
The actual mass of a nucleus is always less than the sum of the masses of the free neutrons and protons that constitute it, the difference being the mass. Nuclei consist of nucleons (neutrons and protons), the total number of which is equal to the mass number of the nucleus. In this fission event, one among billion quadrillion identical ones, the fissionable uraniumatom (nucleus) reacts with a neutron, becomes temporarily unstable and is fragmented verysoon thereafter into a nucleus of barium (Ba) and a nucleus of krypton (Kr). Nuclear reactors produce little waste or spent fuel, and only a small portion of that is highly radioactive. The fission process may be best understood through a consideration of the structure and stability of nuclear matter. Nuclear power plants have the smallest land footprint per unit of electricity at 0.3m2 per megawatt-hour.
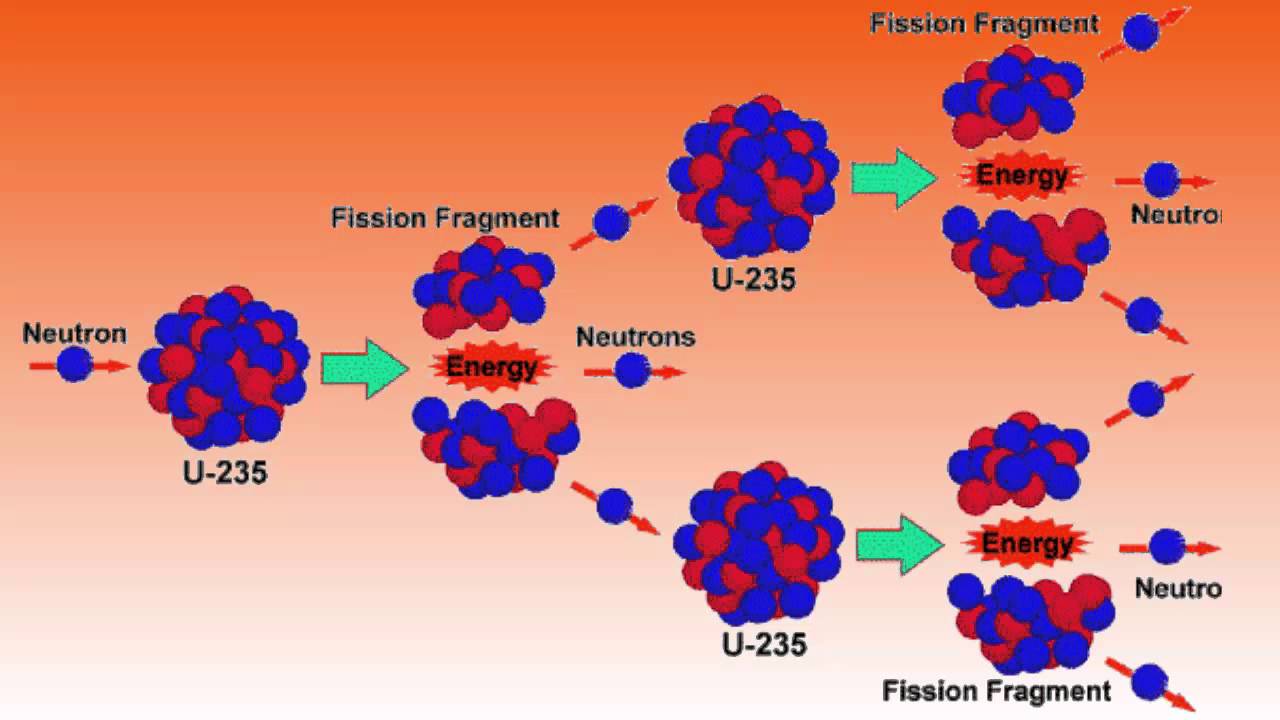
with m is mass (kilograms), c is speed of light (meters/sec. To calculate the energy released during mass destruction in both nuclear fission and fusion, we use Einstein’s equation that equates energy and mass: (7.5.1) E m c 2. Nuclear power has the highest EROI of any energy source, returning 75 units of energy for every unit of energy spent in construction and operation. The mass of an element's nucleus as a whole is less than the total mass of its individual protons and neutrons. The table below compares the energy density of uranium to other fuels, expressed in megajoules of energy contained per kilogram of fuel:Įnriched uranium-235, the fuel used by commercial nuclear reactors, contains 3.9 million megajoules of energy per kilogram of weight, which is magnitudes larger than the energy density of traditional fossil fuels.įor this reason, a relatively small quantity of nuclear fuel can produce significant amounts of energy through fission, translating into various advantages for nuclear power: Nuclear power ultimately stems from the radioactivity of uranium atoms, which yield great amounts of energy when split by the process of fission.īesides the radioactive nature of uranium, its energy density-the amount of energy it contains per unit of mass-is one of its exceptional properties, making it significantly more powerful than other energy fuels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
